Deep learning with tensorflow
Convolutional network
Create data
The data are generated by a python script in Blender :
- 900 point of views for each 54 cards.
- Each generated images as a resolution of 128 * 128.
- A total of 48 600 images.
Create Data with blender
This step require Blender in order to generate the images
- Open TextureCards/cardgames.blend
- Run script (See screenshot below)
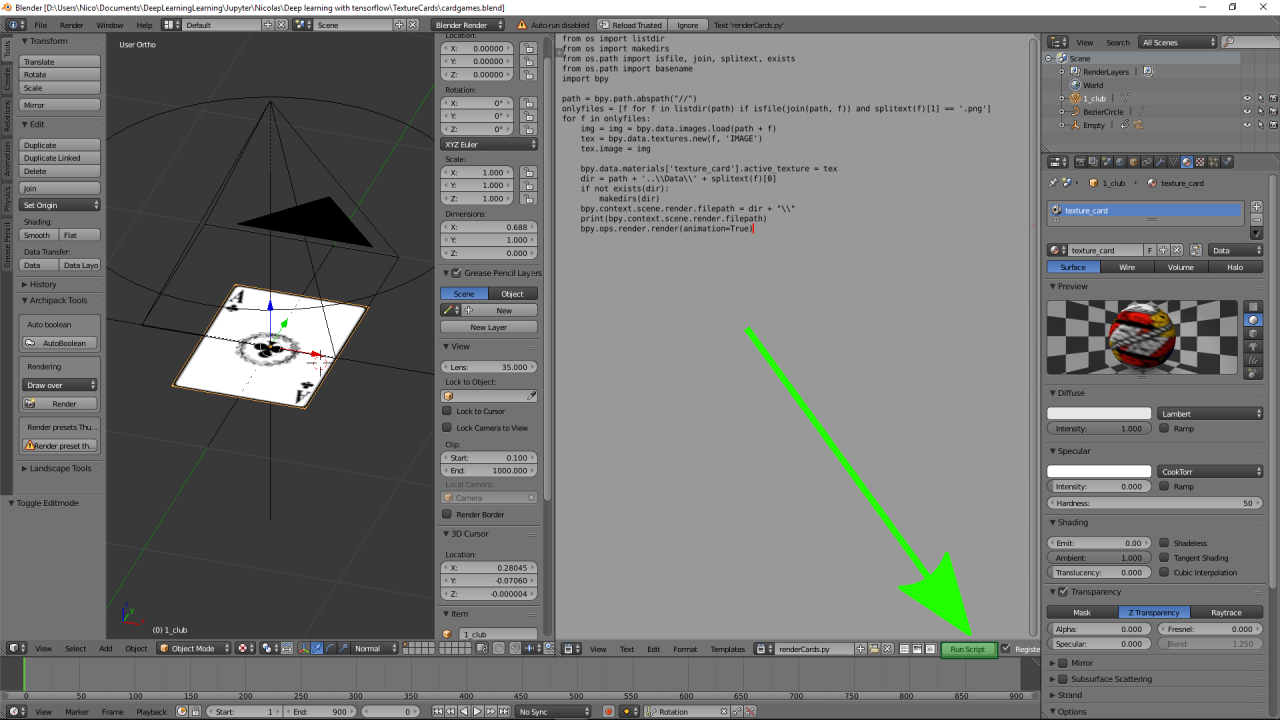
Blender script
from os import listdir
from os import makedirs
from os.path import isfile, join, splitext, exists
from os.path import basename
import bpy
path = bpy.path.abspath("//")
onlyfiles = [f for f in listdir(path) if isfile(join(path, f)) and splitext(f)[1] == '.png']
for f in onlyfiles:
img = img = bpy.data.images.load(path + f)
tex = bpy.data.textures.new(f, 'IMAGE')
tex.image = img
bpy.data.materials['texture_card'].active_texture = tex
dir = path + '..\\Data\\' + splitext(f)[0]
if not exists(dir):
makedirs(dir)
bpy.context.scene.render.filepath = dir + "\\"
bpy.ops.wm.console_toggle()
print(bpy.context.scene.render.filepath)
bpy.ops.render.render(animation=True)
Import datasetlib
**If you want to generate dataset turn create_date to True just below :) **
%run ../importlib.py
import datasetlib
datasetlib.buffer_size = 64000000
create_data = False
importing Jupyter notebook from datasetlib.ipynb
Define label value
label_tab = {
'1_club' : 0, '1_diamond' : 1, '1_heart' : 2, '1_spade' : 3,
'2_club' : 4, '2_diamond' : 5, '2_heart' : 6, '2_spade' : 7,
'3_club' : 8, '3_diamond' : 9, '3_heart' : 10, '3_spade' : 11,
'4_club' : 12, '4_diamond' : 13, '4_heart' : 14, '4_spade' : 15,
'5_club' : 16, '5_diamond' : 17, '5_heart' : 18, '5_spade' : 19,
'6_club' : 20, '6_diamond' : 21, '6_heart' : 22, '6_spade' : 23,
'7_club' : 24, '7_diamond' : 25, '7_heart' : 26, '7_spade' : 27,
'8_club' : 28, '8_diamond' : 29, '8_heart' : 30, '8_spade' : 31,
'9_club' : 32, '9_diamond' : 33, '9_heart' : 34, '9_spade' : 35,
'10_club' : 36, '10_diamond' : 37, '10_heart' : 38, '10_spade' : 39,
'jack_club' : 40, 'jack_diamond' : 41, 'jack_heart' : 42, 'jack_spade' : 43,
'queen_club' : 44, 'queen_diamond' : 45, 'queen_heart' : 46, 'queen_spade' : 47,
'king_club' : 48, 'king_diamond' : 49, 'king_heart' : 50, 'king_spade' : 51,
'joker_red' : 52, 'joker_black' : 53
}
label_array = [
'1_club', '1_diamond', '1_heart', '1_spade',
'2_club', '2_diamond', '2_heart', '2_spade',
'3_club', '3_diamond', '3_heart', '3_spade',
'4_club', '4_diamond', '4_heart', '4_spade',
'5_club', '5_diamond', '5_heart', '5_spade',
'6_club', '6_diamond', '6_heart', '6_spade',
'7_club', '7_diamond', '7_heart', '7_spade',
'8_club', '8_diamond', '8_heart', '8_spade',
'9_club', '9_diamond', '9_heart', '9_spade',
'10_club', '10_diamond', '10_heart', '10_spade',
'jack_club', 'jack_diamond', 'jack_heart', 'jack_spade',
'queen_club', 'queen_diamond', 'queen_heart', 'queen_spade',
'king_club', 'king_diamond', 'king_heart', 'king_spade',
'joker_red', 'joker_black'
]
Define global variables
image_index_filename = 'image_cards.txt'
label_index_filename = 'label_cards.txt'
image_shuffle_index_filename = 'image_shuffle_cards.txt'
label_shuffle_index_filename = 'label_shuffle_cards.txt'
dataset_size = 0
if (create_data == False):
dataset_size = 48600
Generate index and label file
if (create_data == True):
dataset_size = datasetlib.create_index_file(
"Data/**/*.png",
label_tab,
image_index_filename,
label_index_filename)
if (create_data == True):
dataset_size = datasetlib.create_shuffle_index_file(
image_index_filename,
label_index_filename,
image_shuffle_index_filename,
label_shuffle_index_filename)
Generate binary dataset
if (create_data == True):
datasetlib.generate_chunck_dataset_thread(
#souce file
label_shuffle_index_filename,
#number data per chunck
10000,
#number max of thread
8,
#number of chunck, -1 for automatic maximum chunck
-1,
#binary type 0 for image, 1 for label
1)
if (create_data == True):
datasetlib.generate_dataset(label_shuffle_index_filename, dataset_size, 0, 1)
if (create_data == True):
datasetlib.generate_chunck_dataset_thread(
#souce file
image_shuffle_index_filename,
#number data per chunck
10000,
#number max of thread
8,
#number of chunck, -1 for automatic maximum chunck
-1,
#binary type 0 for image, 1 for label
0)
if (create_data == True):
datasetlib.generate_dataset(image_shuffle_index_filename, dataset_size)
Configuration of Neural Network
import tensorflow as tf
import time
import numpy as np
print(tf.__version__)
1.4.0
# Convolutional Layer 1.
filter_size1 = 5 # Convolution filters are 5 x 5 pixels.
num_filters1 = 16 # There are 16 of these filters.
# Convolutional Layer 2.
filter_size2 = 3 # Convolution filters are 5 x 5 pixels.
num_filters2 = 64 # There are 36 of these filters.
filter_size3 = 3 # Convolution filters are 5 x 5 pixels.
num_filters3 = 256 # There are 36 of these filters.
filter_size4 = 3 # Convolution filters are 5 x 5 pixels.
num_filters4 = 512 # There are 36 of these filters.
filter_size5 = 5 # Convolution filters are 5 x 5 pixels.
num_filters5 = 512
# Fully-connected layer.
fc_size = 512 # Number of neurons in fully-connected layer.
Data dimention
# We know that MNIST images are 28 pixels in each dimension.
img_size = 128
# Images are stored in one-dimensional arrays of this length.
img_size_flat = img_size * img_size
# Tuple with height and width of images used to reshape arrays.
img_shape = (img_size, img_size, 3)
# Number of colour channels for the images: 1 channel for gray-scale.
num_channels = 3
# Number of classes, one class for each of 10 digits.
num_classes = 54
Load data with tensorflow
from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets import base
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
from datetime import timedelta
dataset_image_file = "image_shuffle_cards.ubyte"
dataset_label_file = "label_shuffle_cards.ubyte"
def dense_to_one_hot(labels_dense, num_classes):
num_labels = labels_dense.shape[0]
index_offset = np.arange(num_labels) * num_classes
labels_one_hot = np.zeros((num_labels, num_classes))
labels_one_hot.flat[index_offset + labels_dense.ravel()] = 1
return labels_one_hot
class Datasets(object):
def __init__(self,
images,
labels):
self._num_examples = images.shape[0]
images = images.reshape(images.shape[0], images.shape[1] * images.shape[2], images.shape[3])
self._images = images
self._labels_true = labels
self._labels = dense_to_one_hot(labels, num_classes)
self._epochs_completed = 0
self._index_in_epoch = 0
@property
def images(self):
return self._images
@property
def num_examples(self):
return self._num_examples
@property
def labels(self):
return self._labels
@property
def labels_true(self):
return self._labels_true
@property
def epochs_completed(self):
return self._epochs_completed
def next_batch(self, batch_size):
"""Return the next `batch_size` examples from this data set."""
start = self._index_in_epoch
self._index_in_epoch += batch_size
if self._index_in_epoch > self._num_examples:
# Finished epoch
self._epochs_completed += 1
# Shuffle the data
perm = np.arange(self._num_examples)
np.random.shuffle(perm)
self._images = self._images[perm]
self._labels = self._labels[perm]
# Start next epoch
start = 0
self._index_in_epoch = batch_size
assert batch_size <= self._num_examples
end = self._index_in_epoch
return self._images[start:end], self._labels[start:end]
def load_data(source, label, number, offset=0):
images = datasetlib.read_image_data(source, num_channels, number, offset)
labels = datasetlib.read_label_data(label, number, offset)
train = Datasets(images, labels)
test = Datasets(images, labels)
return base.Datasets(train=train, validation=train, test=test)
# generate_ubyte_file(dataset_image_shuffle, 100)
dataset = load_data(dataset_image_file, dataset_label_file, dataset_size)
print(dataset)
Datasets(train=<__main__.Datasets object at 0x000001AA95E532B0>, validation=<__main__.Datasets object at 0x000001AA95E532B0>, test=<__main__.Datasets object at 0x000001AA95E532E8>)
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_images(images, cls_true, cls_pred=None):
assert len(images) == len(cls_true) == 9
# Create figure with 3x3 sub-plots.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3)
fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.6, wspace=0.3)
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
# Plot image.
ax.imshow(images[i].reshape(img_shape), cmap='binary')
# Show true and predicted classes.
if cls_pred is None:
xlabel = "True: {0}".format(label_array[cls_true[i]])
else:
xlabel = "True: {0}\n Pred: {1}".format(label_array[cls_true[i]], label_array[cls_pred[i]])
# Show the classes as the label on the x-axis.
ax.set_xlabel(xlabel)
# Remove ticks from the plot.
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
# Ensure the plot is shown correctly with multiple plots
# in a single Notebook cell.
plt.show()
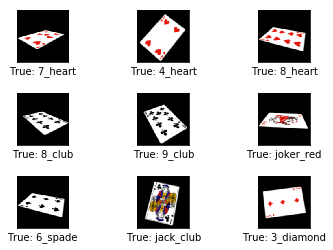
# Get the first images from the test-set.
images = dataset.train.images[0:9]
# Get the true classes for those images.
cls_true = dataset.train.labels_true[0:9]
# Plot the images and labels using our helper-function above.
plot_images(images=images, cls_true=cls_true)
dataset.test.cls = np.argmax(dataset.test.labels, axis=1)
TensorFlow graph
def new_weights(shape):
return tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.05))
def new_biases(length):
return tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.05, shape=[length]))
def new_conv_layer(input, # The previous layer.
num_input_channels, # Num. channels in prev. layer.
filter_size, # Width and height of each filter.
num_filters, # Number of filters.
use_pooling=True): # Use 2x2 max-pooling.
# Shape of the filter-weights for the convolution.
# This format is determined by the TensorFlow API.
shape = [filter_size, filter_size, num_input_channels, num_filters]
# Create new weights aka. filters with the given shape.
weights = new_weights(shape=shape)
# Create new biases, one for each filter.
biases = new_biases(length=num_filters)
# Create the TensorFlow operation for convolution.
# Note the strides are set to 1 in all dimensions.
# The first and last stride must always be 1,
# because the first is for the image-number and
# the last is for the input-channel.
# But e.g. strides=[1, 2, 2, 1] would mean that the filter
# is moved 2 pixels across the x- and y-axis of the image.
# The padding is set to 'SAME' which means the input image
# is padded with zeroes so the size of the output is the same.
layer = tf.nn.conv2d(input=input,
filter=weights,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='SAME')
# Add the biases to the results of the convolution.
# A bias-value is added to each filter-channel.
layer += biases
# Use pooling to down-sample the image resolution?
if use_pooling:
# This is 2x2 max-pooling, which means that we
# consider 2x2 windows and select the largest value
# in each window. Then we move 2 pixels to the next window.
layer = tf.nn.max_pool(value=layer,
ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1],
padding='SAME')
# Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU).
# It calculates max(x, 0) for each input pixel x.
# This adds some non-linearity to the formula and allows us
# to learn more complicated functions.
layer = tf.nn.relu(layer)
# Note that ReLU is normally executed before the pooling,
# but since relu(max_pool(x)) == max_pool(relu(x)) we can
# save 75% of the relu-operations by max-pooling first.
# We return both the resulting layer and the filter-weights
# because we will plot the weights later.
return layer, weights
def flatten_layer(layer):
# Get the shape of the input layer.
layer_shape = layer.get_shape()
# The shape of the input layer is assumed to be:
# layer_shape == [num_images, img_height, img_width, num_channels]
# The number of features is: img_height * img_width * num_channels
# We can use a function from TensorFlow to calculate this.
num_features = layer_shape[1:4].num_elements()
# Reshape the layer to [num_images, num_features].
# Note that we just set the size of the second dimension
# to num_features and the size of the first dimension to -1
# which means the size in that dimension is calculated
# so the total size of the tensor is unchanged from the reshaping.
layer_flat = tf.reshape(layer, [-1, num_features])
# The shape of the flattened layer is now:
# [num_images, img_height * img_width * num_channels]
# Return both the flattened layer and the number of features.
return layer_flat, num_features
def new_fc_layer(input, # The previous layer.
num_inputs, # Num. inputs from prev. layer.
num_outputs, # Num. outputs.
use_relu=True): # Use Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)?
# Create new weights and biases.
weights = new_weights(shape=[num_inputs, num_outputs])
biases = new_biases(length=num_outputs)
# Calculate the layer as the matrix multiplication of
# the input and weights, and then add the bias-values.
layer = tf.matmul(input, weights) + biases
# Use ReLU?
if use_relu:
layer = tf.nn.relu(layer)
return layer
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, img_size_flat, num_channels], name='x')
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, img_size, img_size, num_channels])
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, num_classes], name='y_true')
y_true_cls = tf.argmax(y_true, dimension=1)
WARNING:tensorflow:From <ipython-input-25-71ccadb4572d>:1: calling argmax (from tensorflow.python.ops.math_ops) with dimension is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Use the `axis` argument instead
layer_conv1, weights_conv1 = \
new_conv_layer(input=x_image,
num_input_channels=num_channels,
filter_size=filter_size1,
num_filters=num_filters1,
use_pooling=False)
layer_conv1
<tf.Tensor 'Relu:0' shape=(?, 128, 128, 16) dtype=float32>
layer_conv2, weights_conv2 = \
new_conv_layer(input=layer_conv1,
num_input_channels=num_filters1,
filter_size=filter_size2,
num_filters=num_filters2,
use_pooling=True)
layer_conv2
<tf.Tensor 'Relu_1:0' shape=(?, 64, 64, 64) dtype=float32>
layer_conv3, weights_conv3 = \
new_conv_layer(input=layer_conv2,
num_input_channels=num_filters2,
filter_size=filter_size3,
num_filters=num_filters3,
use_pooling=True)
layer_conv3
<tf.Tensor 'Relu_2:0' shape=(?, 32, 32, 256) dtype=float32>
layer_conv4, weights_conv4 = \
new_conv_layer(input=layer_conv3,
num_input_channels=num_filters3,
filter_size=filter_size4,
num_filters=num_filters4,
use_pooling=True)
layer_conv4
<tf.Tensor 'Relu_3:0' shape=(?, 16, 16, 512) dtype=float32>
layer_conv5, weights_conv5 = \
new_conv_layer(input=layer_conv4,
num_input_channels=num_filters4,
filter_size=filter_size3,
num_filters=num_filters3,
use_pooling=True)
layer_conv5
<tf.Tensor 'Relu_4:0' shape=(?, 8, 8, 256) dtype=float32>
layer_flat, num_features = flatten_layer(layer_conv5)
layer_flat
<tf.Tensor 'Reshape_1:0' shape=(?, 16384) dtype=float32>
num_features
16384
layer_fc1 = new_fc_layer(input=layer_flat,
num_inputs=num_features,
num_outputs=fc_size,
use_relu=True)
layer_fc1
<tf.Tensor 'Relu_5:0' shape=(?, 512) dtype=float32>
layer_fc2 = new_fc_layer(input=layer_fc1,
num_inputs=fc_size,
num_outputs=num_classes,
use_relu=False)
layer_fc2
<tf.Tensor 'add_6:0' shape=(?, 54) dtype=float32>
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(layer_fc2)
y_pred_cls = tf.argmax(y_pred, dimension=1)
cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=layer_fc2,
labels=y_true)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
learning_rate = 1e-3
k = 0.65
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate, global_step, 100, k)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost, global_step=global_step)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(y_pred_cls, y_true_cls)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
session = tf.Session()
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
train_batch_size = 128
# Counter for total number of iterations performed so far.
total_iterations = 0
max_acc = 0.9
def optimize(num_iterations):
# Ensure we update the global variable rather than a local copy.
global total_iterations
global max_acc
# Start-time used for printing time-usage below.
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(total_iterations,
total_iterations + num_iterations):
# Get a batch of training examples.
# x_batch now holds a batch of images and
# y_true_batch are the true labels for those images.
x_batch, y_true_batch = dataset.train.next_batch(train_batch_size)
# Put the batch into a dict with the proper names
# for placeholder variables in the TensorFlow graph.
feed_dict_train = {x: x_batch,
y_true: y_true_batch}
# Run the optimizer using this batch of training data.
# TensorFlow assigns the variables in feed_dict_train
# to the placeholder variables and then runs the optimizer.
session.run(optimizer, feed_dict=feed_dict_train)
# Print status every 100 iterations.
if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
# Calculate the accuracy on the training-set.
acc = session.run(accuracy, feed_dict=feed_dict_train)
# Message for printing.
msg = "Optimization Iteration: {0:>6}, Training Accuracy: {1:>6.1%}"
# Print it.
print(msg.format(i + 1, acc), " - learning rate => ", session.run(learning_rate))
if (acc > max_acc):
max_acc = acc
save_path = saver.save(session, "./tensorflowModels/cards/model.ckpt")
print("Model saved in file: %s" % save_path)
else:
# Message for printing.
msg = "Optimization Iteration: {0:>6}, Training Accuracy: {1:>6.1%}"
print()
# Print it.
print(msg.format(i + 1, acc), " - learning rate => ", session.run(learning_rate))
# Update the total number of iterations performed.
total_iterations += num_iterations
# Ending time.
end_time = time.time()
# Difference between start and end-times.
time_dif = end_time - start_time
# Print the time-usage.
print("Time usage: " + str(timedelta(seconds=int(round(time_dif)))))
def plot_example_errors(cls_pred, correct):
# This function is called from print_test_accuracy() below.
# cls_pred is an array of the predicted class-number for
# all images in the test-set.
# correct is a boolean array whether the predicted class
# is equal to the true class for each image in the test-set.
# Negate the boolean array.
incorrect = (correct == False)
# Get the images from the test-set that have been
# incorrectly classified.
images = dataset.test.images[incorrect]
# Get the predicted classes for those images.
cls_pred = cls_pred[incorrect]
# Get the true classes for those images.
cls_true = dataset.test.cls[incorrect]
# Plot the first 9 images.
plot_images(images=images[0:9],
cls_true=cls_true[0:9],
cls_pred=cls_pred[0:9])
def plot_confusion_matrix(cls_pred):
# This is called from print_test_accuracy() below.
# cls_pred is an array of the predicted class-number for
# all images in the test-set.
# Get the true classifications for the test-set.
cls_true = dataset.test.cls
# Get the confusion matrix using sklearn.
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true=cls_true,
y_pred=cls_pred)
# Print the confusion matrix as text.
print(cm)
# Plot the confusion matrix as an image.
plt.matshow(cm)
# Make various adjustments to the plot.
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(num_classes)
plt.xticks(tick_marks, range(num_classes))
plt.yticks(tick_marks, range(num_classes))
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('True')
# Ensure the plot is shown correctly with multiple plots
# in a single Notebook cell.
plt.show()
# Split the test-set into smaller batches of this size.
test_batch_size = 256
def print_test_accuracy(show_example_errors=False,
show_confusion_matrix=False):
# Number of images in the test-set.
num_test = len(dataset.test.images)
# Allocate an array for the predicted classes which
# will be calculated in batches and filled into this array.
cls_pred = np.zeros(shape=num_test, dtype=np.int)
# Now calculate the predicted classes for the batches.
# We will just iterate through all the batches.
# There might be a more clever and Pythonic way of doing this.
# The starting index for the next batch is denoted i.
i = 0
while i < num_test:
# The ending index for the next batch is denoted j.
j = min(i + test_batch_size, num_test)
# Get the images from the test-set between index i and j.
images = dataset.test.images[i:j, :]
# Get the associated labels.
labels = dataset.test.labels[i:j, :]
# Create a feed-dict with these images and labels.
feed_dict = {x: images,
y_true: labels}
# Calculate the predicted class using TensorFlow.
cls_pred[i:j] = session.run(y_pred_cls, feed_dict=feed_dict)
# Set the start-index for the next batch to the
# end-index of the current batch.
i = j
# Convenience variable for the true class-numbers of the test-set.
cls_true = dataset.test.cls
# Create a boolean array whether each image is correctly classified.
correct = (cls_true == cls_pred)
# Calculate the number of correctly classified images.
# When summing a boolean array, False means 0 and True means 1.
correct_sum = correct.sum()
# Classification accuracy is the number of correctly classified
# images divided by the total number of images in the test-set.
acc = float(correct_sum) / num_test
# Print the accuracy.
msg = "Accuracy on Test-Set: {0:.1%} ({1} / {2})"
print(msg.format(acc, correct_sum, num_test))
# Plot some examples of mis-classifications, if desired.
if show_example_errors:
print("Example errors:")
plot_example_errors(cls_pred=cls_pred, correct=correct)
# Plot the confusion matrix, if desired.
if show_confusion_matrix:
print("Confusion Matrix:")
plot_confusion_matrix(cls_pred=cls_pred)
import math
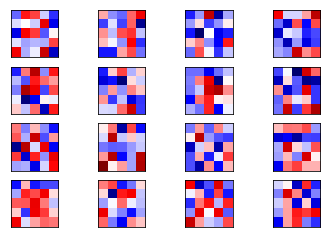
def plot_conv_weights(weights, input_channel=0):
# Assume weights are TensorFlow ops for 4-dim variables
# e.g. weights_conv1 or weights_conv2.
# Retrieve the values of the weight-variables from TensorFlow.
# A feed-dict is not necessary because nothing is calculated.
w = session.run(weights)
# Get the lowest and highest values for the weights.
# This is used to correct the colour intensity across
# the images so they can be compared with each other.
w_min = np.min(w)
w_max = np.max(w)
# Number of filters used in the conv. layer.
num_filters = w.shape[3]
# Number of grids to plot.
# Rounded-up, square-root of the number of filters.
num_grids = math.ceil(math.sqrt(num_filters))
# Create figure with a grid of sub-plots.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_grids, num_grids)
# Plot all the filter-weights.
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
# Only plot the valid filter-weights.
if i<num_filters:
# Get the weights for the i'th filter of the input channel.
# See new_conv_layer() for details on the format
# of this 4-dim tensor.
img = w[:, :, input_channel, i]
# Plot image.
ax.imshow(img, vmin=w_min, vmax=w_max,
interpolation='nearest', cmap='seismic')
# Remove ticks from the plot.
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
# Ensure the plot is shown correctly with multiple plots
# in a single Notebook cell.
plt.show()
def plot_conv_layer(layer, image):
# Assume layer is a TensorFlow op that outputs a 4-dim tensor
# which is the output of a convolutional layer,
# e.g. layer_conv1 or layer_conv2.
# Create a feed-dict containing just one image.
# Note that we don't need to feed y_true because it is
# not used in this calculation.
feed_dict = {x: [image]}
# Calculate and retrieve the output values of the layer
# when inputting that image.
values = session.run(layer, feed_dict=feed_dict)
# Number of filters used in the conv. layer.
num_filters = values.shape[3]
# Number of grids to plot.
# Rounded-up, square-root of the number of filters.
num_grids = math.ceil(math.sqrt(num_filters))
# Create figure with a grid of sub-plots.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_grids, num_grids)
# Plot the output images of all the filters.
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
# Only plot the images for valid filters.
if i<num_filters:
# Get the output image of using the i'th filter.
# See new_conv_layer() for details on the format
# of this 4-dim tensor.
img = values[0, :, :, i]
# Plot image.
ax.imshow(img, interpolation='nearest', cmap='binary')
# Remove ticks from the plot.
ax.set_xticks([])
ax.set_yticks([])
# Ensure the plot is shown correctly with multiple plots
# in a single Notebook cell.
plt.show()
def plot_image(image):
plt.imshow(image.reshape(img_shape),
interpolation='nearest',
cmap='binary')
plt.show()
Start training
saver = tf.train.Saver()
builder = tf.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder('./tensorflowModels/cards/model/')
builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(session,
[tf.saved_model.tag_constants.TRAINING],
signature_def_map=None,
assets_collection=None)
INFO:tensorflow:No assets to save.
INFO:tensorflow:No assets to write.
optimize(num_iterations=3000)
Optimization Iteration: 100, Training Accuracy: 36.7% - learning rate => 0.00065
Optimization Iteration: 200, Training Accuracy: 80.5% - learning rate => 0.0004225
Optimization Iteration: 300, Training Accuracy: 90.6% - learning rate => 0.000274625
Model saved in file: ./tensorflowModels/cards/model.ckpt
Optimization Iteration: 400, Training Accuracy: 96.1% - learning rate => 0.000178506
Model saved in file: ./tensorflowModels/cards/model.ckpt
Optimization Iteration: 500, Training Accuracy: 97.7% - learning rate => 0.000116029
Model saved in file: ./tensorflowModels/cards/model.ckpt
Optimization Iteration: 600, Training Accuracy: 96.1% - learning rate => 7.54189e-05
Optimization Iteration: 700, Training Accuracy: 96.9% - learning rate => 4.90223e-05
Optimization Iteration: 800, Training Accuracy: 97.7% - learning rate => 3.18645e-05
Optimization Iteration: 900, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 2.07119e-05
Model saved in file: ./tensorflowModels/cards/model.ckpt
Optimization Iteration: 1000, Training Accuracy: 97.7% - learning rate => 1.34627e-05
Optimization Iteration: 1100, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 8.75078e-06
Model saved in file: ./tensorflowModels/cards/model.ckpt
Optimization Iteration: 1200, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 5.68801e-06
Optimization Iteration: 1300, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 3.6972e-06
Optimization Iteration: 1400, Training Accuracy: 96.9% - learning rate => 2.40318e-06
Optimization Iteration: 1500, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 1.56207e-06
Optimization Iteration: 1600, Training Accuracy: 96.9% - learning rate => 1.01534e-06
Optimization Iteration: 1700, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 6.59974e-07
Optimization Iteration: 1800, Training Accuracy: 97.7% - learning rate => 4.28983e-07
Optimization Iteration: 1900, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 2.78839e-07
Optimization Iteration: 2000, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 1.81245e-07
Optimization Iteration: 2100, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 1.17809e-07
Optimization Iteration: 2200, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 7.65761e-08
Optimization Iteration: 2300, Training Accuracy: 98.4% - learning rate => 4.97745e-08
Optimization Iteration: 2400, Training Accuracy: 100.0% - learning rate => 3.23534e-08
Optimization Iteration: 2500, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 2.10297e-08
Optimization Iteration: 2600, Training Accuracy: 97.7% - learning rate => 1.36693e-08
Optimization Iteration: 2700, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 8.88506e-09
Optimization Iteration: 2800, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 5.77529e-09
Optimization Iteration: 2900, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 3.75394e-09
Optimization Iteration: 3000, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 2.44006e-09
Optimization Iteration: 3000, Training Accuracy: 99.2% - learning rate => 2.44006e-09
Time usage: 0:34:47
print_test_accuracy(show_example_errors=True)
Accuracy on Test-Set: 99.2% (48192 / 48600)
Example errors:
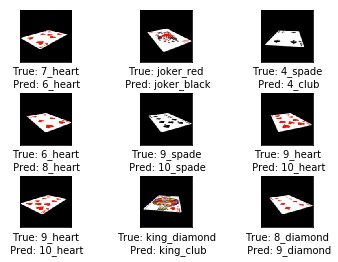
image1 = dataset.test.images[0]
print(label_array[dataset.test.labels_true[0]])
plot_image(image1)
7_heart

plot_conv_weights(weights=weights_conv1)
plot_conv_layer(layer=layer_conv1, image=image1)
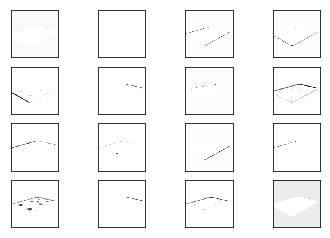
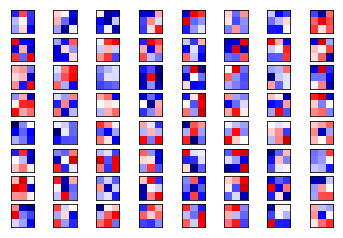
plot_conv_weights(weights=weights_conv2, input_channel=0)
plot_conv_layer(layer=layer_conv2, image=image1)
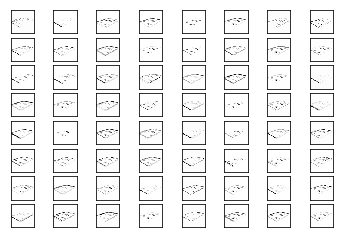
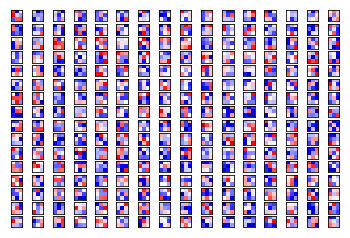
plot_conv_weights(weights=weights_conv3, input_channel=0)
plot_conv_layer(layer=layer_conv3, image=image1)

plot_conv_weights(weights=weights_conv4, input_channel=0)
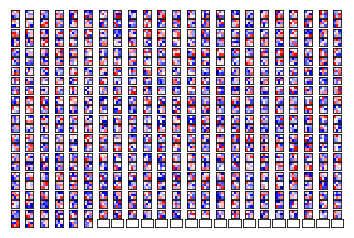
plot_conv_layer(layer=layer_conv4, image=image1)
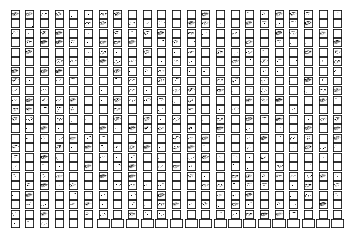
save_path = saver.save(session, "./tensorflowModels/cards/final.ckpt")
print("Model saved in file: %s" % save_path)
builder.save()
Model saved in file: ./tensorflowModels/cards/final.ckpt
INFO:tensorflow:SavedModel written to: b'./tensorflowModels/cards/model/saved_model.pb'
b'./tensorflowModels/cards/model/saved_model.pb'